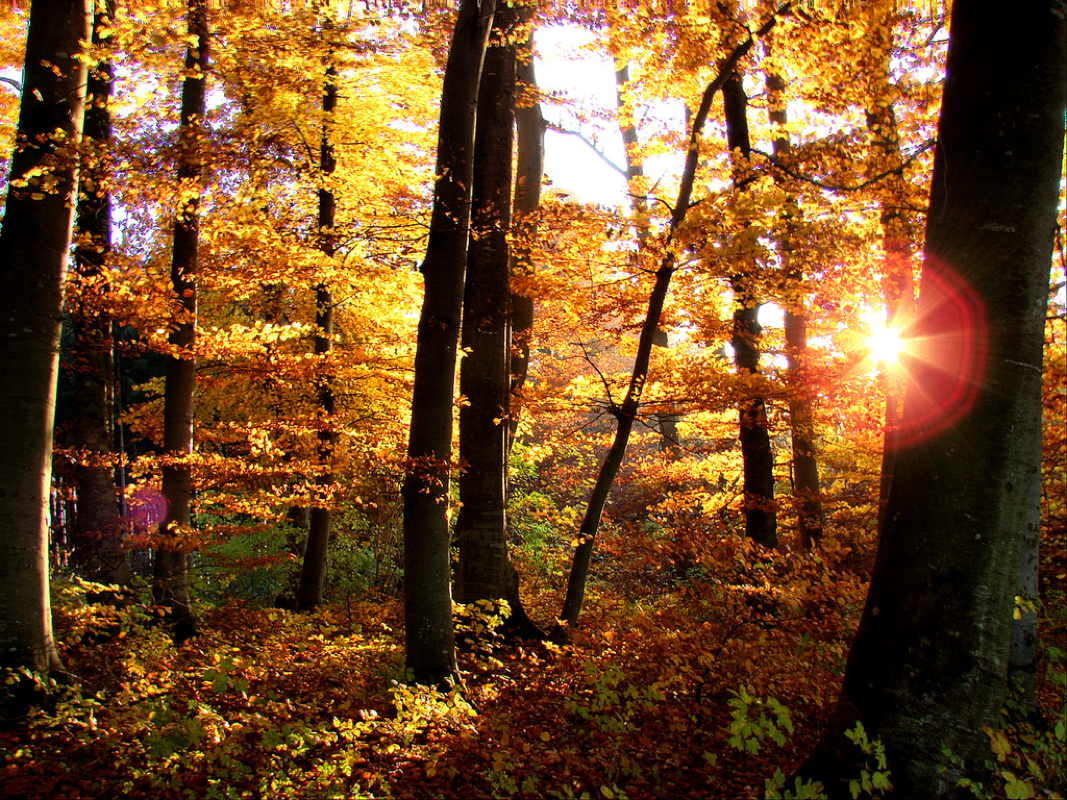
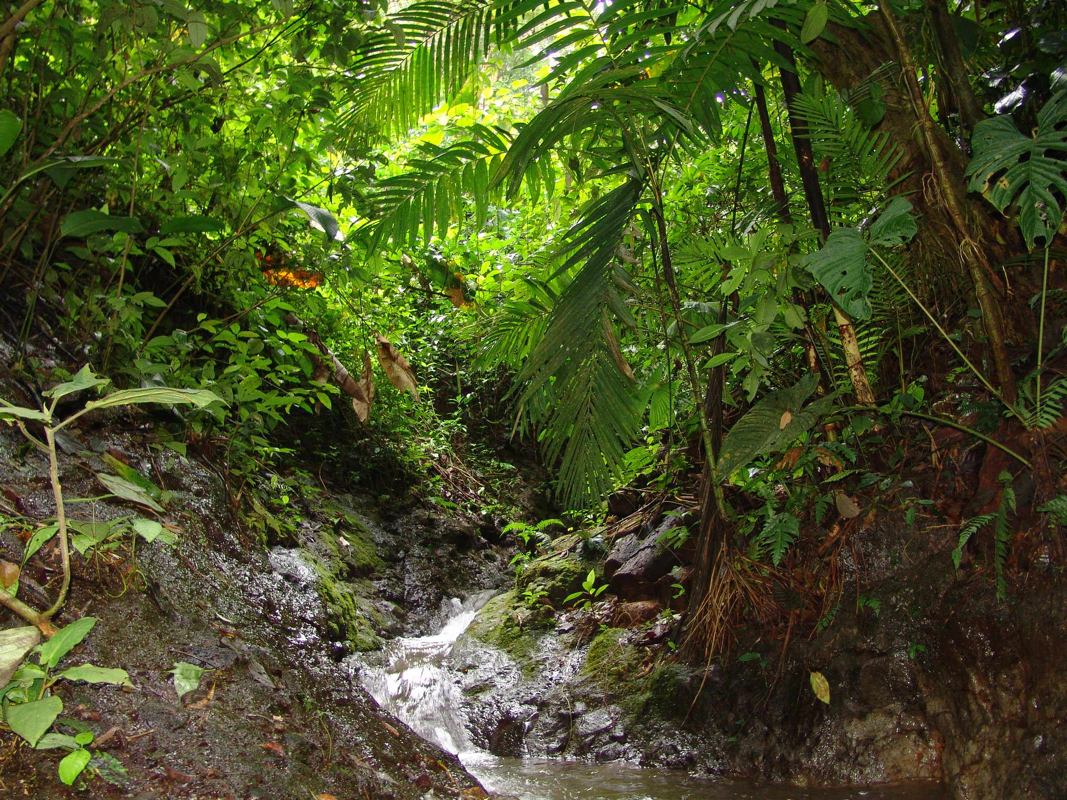
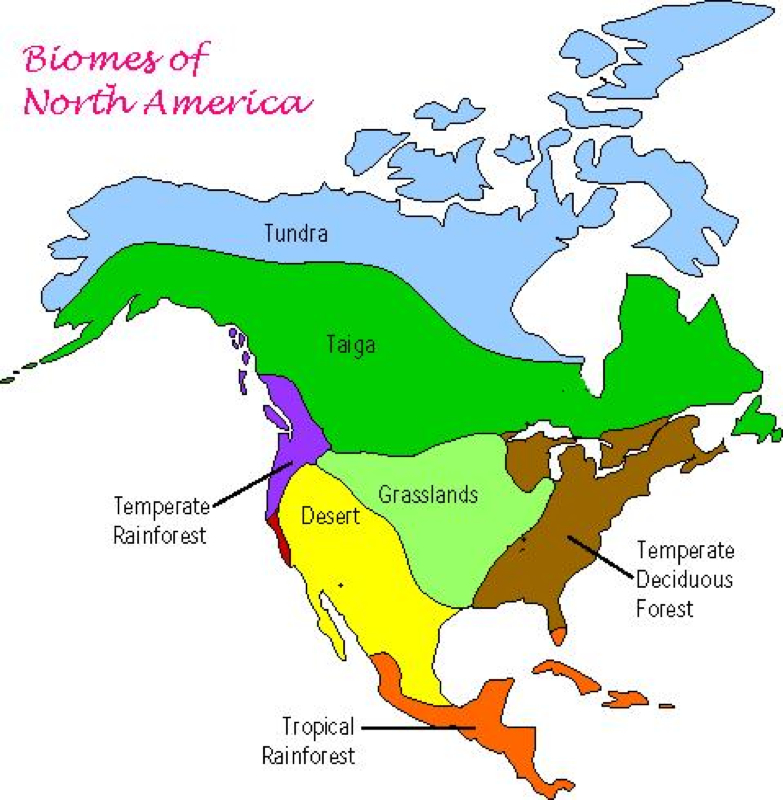
Across the middle latitudes, temperate forests grow where winters are short and 75 to 150 centimeters of precipitation fall each year. Most temperate forests are made up of deciduous trees, sometimes referred to as broadleaf trees.Near the equator, there are no winters. There, tropical forests grow where 200 to 450 centimeters of rain fall each year. The tropical rain forest is the wettest land biome.
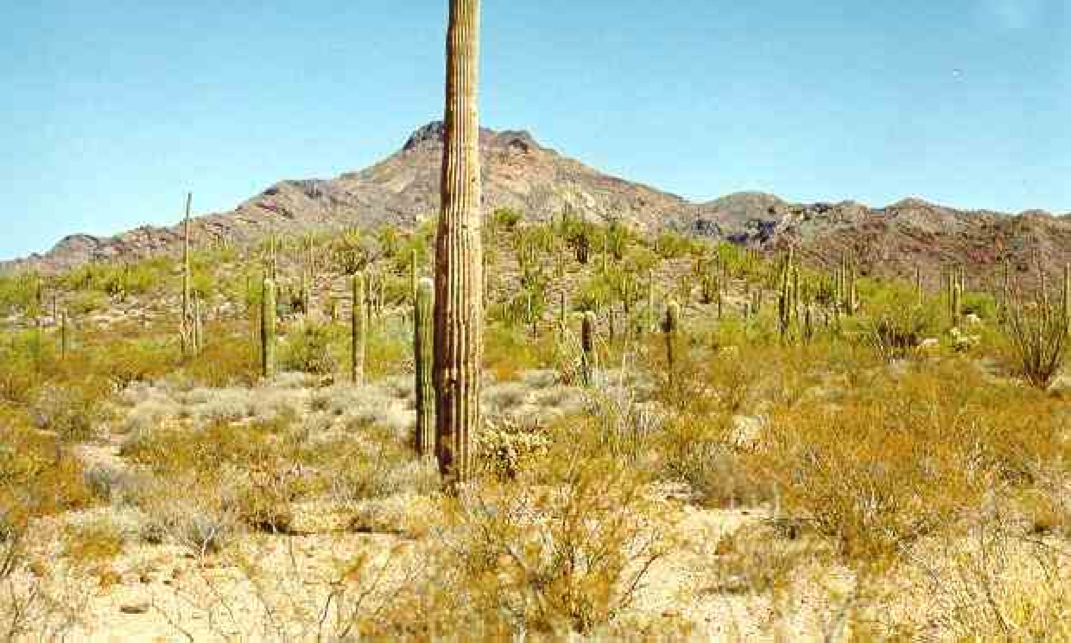
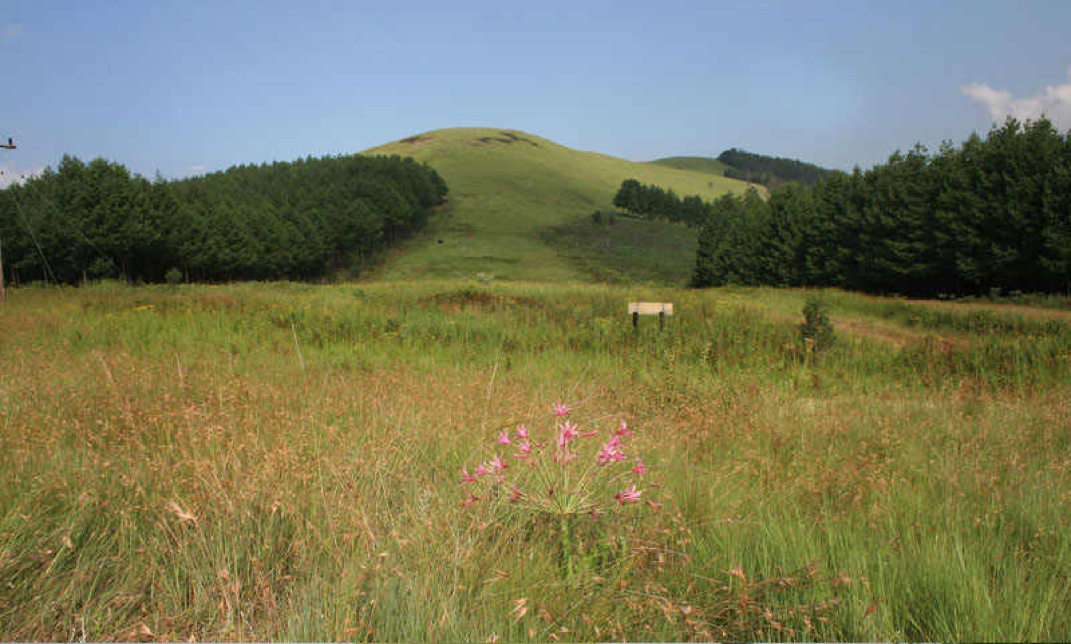
These biomes are found toward the middle latitudes. What deserts and grasslands have in common is that they do not get enough precipitation to support trees.some deserts are cold and some deserts are hot, but all deserts are characterized by their dry soil. Less than 25 centimeters of rain falls each year in a desert. Grassland ecosystems develop in areas of moderate rainfall, generally from 50 to 90 centimeters each year. There is enough rain to support grasses, but too little rain to support forests
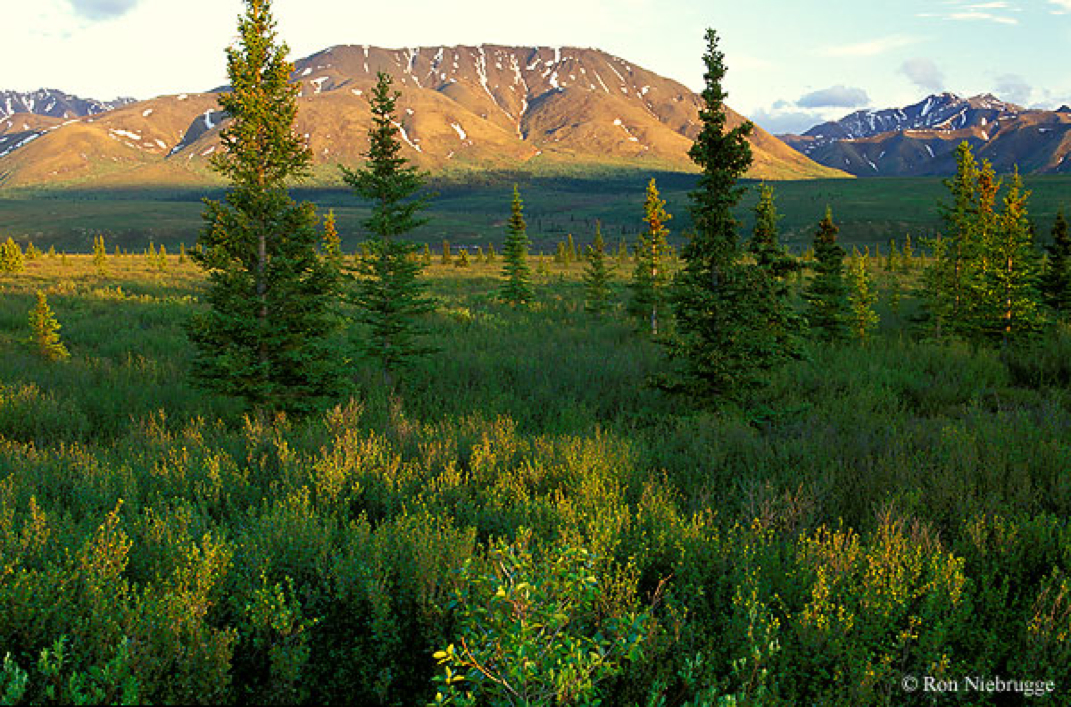
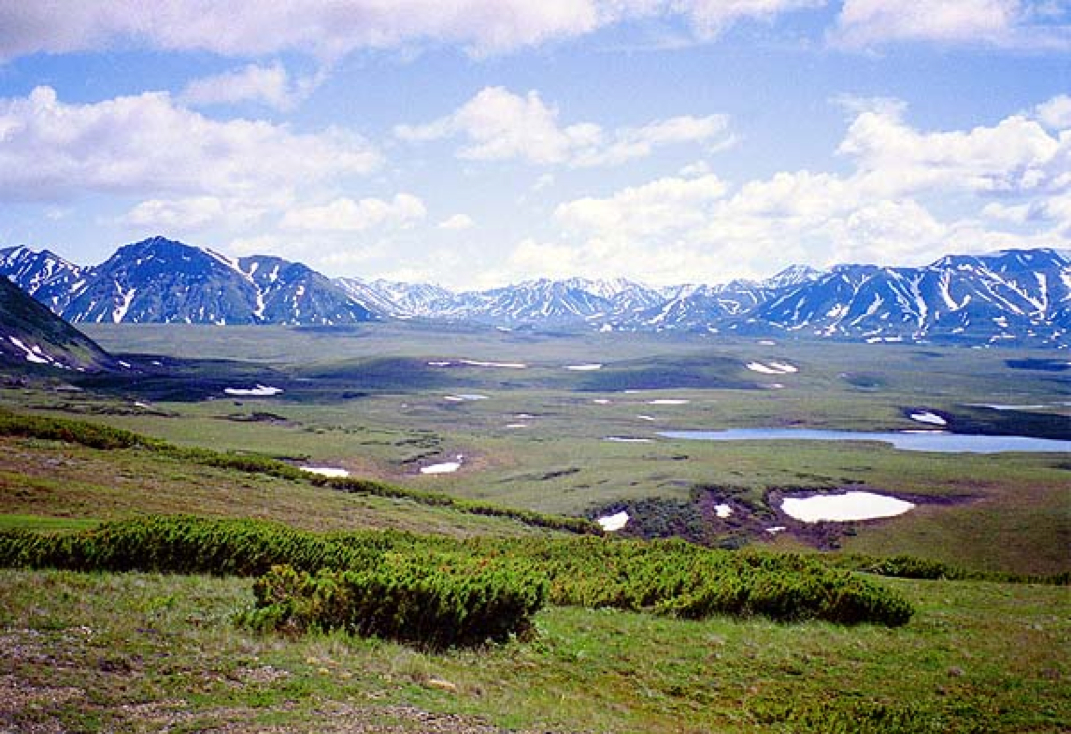
If you go to the northernmost regions of Earth, you will find two biomes- tundra and taiga- that are characterized by long cold winters and short cool summers. The tundra doesn't get much precipitation less than 25 centimeters each year. Yet the area is wet because cold temperatures keep the water from evaporating. Taiga has more precipitation, 30 to 60 centimeters a year. Taiga ecosystems are characterized by evergreen trees called coniferous trees.
Biomes: A region of Earth that has a particular climate and an certain types of plants. Examples are tundra, taiga, desert, grassland, deciduous and tropical forest.
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed